Yuliia Chabak
Priazovskyi State Technical University, Ukraine
Title: Carbides coatings deposited by new pulsed plasma technique
Biography
Biography: Yuliia Chabak
Abstract
Statement of the Problem: Pulsed plasma treatment (PPT) is known for using for surface hardening of machine parts and tools. PPT is usually focused to modify the treated surface due to high speed of heating and cooling followed by the formation of fine crystalline martensite with increased hardness and wear performance. PPT with the use of electro-thermal axial plasma accelerator (ETPA) is quite new technique allowing to deposit the protective coatings with required properties depending on cathode material. Up to now, high-carbon alloyed steels and white cast irons were not used as the cathode material for ETPA plasma processing. The purpose of this study is to study the structure and properties of carbides coating formed using high-Cr cast iron and high-W high speed steel (HSS)
.
Methodology & Theoretical Orientation: The coatings were manufactured applying ETPA device. As the electrode material 28%Cr cast iron and 18%W T1HSS were used. The study was performed employing SEM, EDS, XRD, microhardness testing, after PPT post-heat treatment (950oC, 2 h) was used for structure improving.
Findings: Fe-C-Cr(W) and Fe-C-Cr-W coatings of 150-200 mm thickness were pulse plasma deposited using ETPA. Changing cathode material allowed to form layered coating structure which is coherent to substrate. Post-deposition heat treatment results in precipitation of Cr- and W-rich carbides phases M7C3, M3C2, M6C, M2C followed by the transformation of austenite into martensite. It was found that PPT using ETPA is accompanied with carbon enrichment of the coating which results in increasing carbides volume fraction to 50-70 %. This causes sharp increase of coating microhardness up to 1200-1500 HV.
Conclusion & Significance: PPT with ETPA combining post-heat treatment can be successfully applied for carbides coating deposition which is perspective approach for wear resistance improvement.
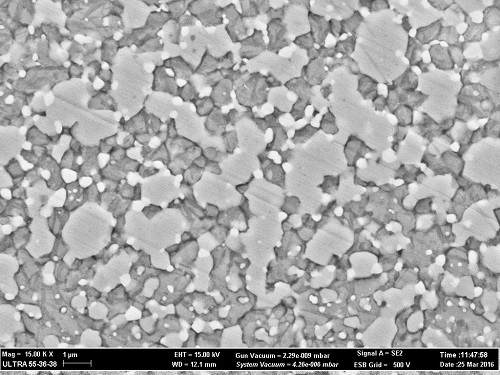
Figure 1: The W-rich carbides in the coating deposited using the cathode of T1 HSS
Recent Publications :
- Espallargas N, Mischler S (2011) Dry waer tribocorrosion mechanisms of pulse plasma nitrided NiCr. Wear 270: 464-471.
- Kolyada Yu, Fedun V (2015) Pulse electrothermal plasma accelerators and its application in scientific researches. Problems of Atomic Science and Technology 4: 325-330.
- Ozbek Y, Akbulut H, Durman M (2015) Surface behavior of AISI 4140 modified with the pulsed-plasma technique. Materials and Technology 49:441-445.
- Efremenko V, Chabak Yu, Lekatou A., Karantzalis A, Shimizu K, Fedun V, Azarkhov A, Efremenko A (20016). Pulsed plasma deposition of Fe-C-Cr-W coating on high-Cr-cast iron: Effect of layered morphology and heat treatment on the microstructure and hardness. Surface and Coatings Technology 304: 293–305.
- Chabak Yu, Fedun V, Shimizu K, Zurnadgy V, Efremenko V (2016) Phase-structural composition of coating obtained by pulsed plasma treatment using eroded cathode of T1 high speed steel. Problems of Atomic Science and Technology 102:102-106.


